Most advanced synthetic human embryos yet spark controversy
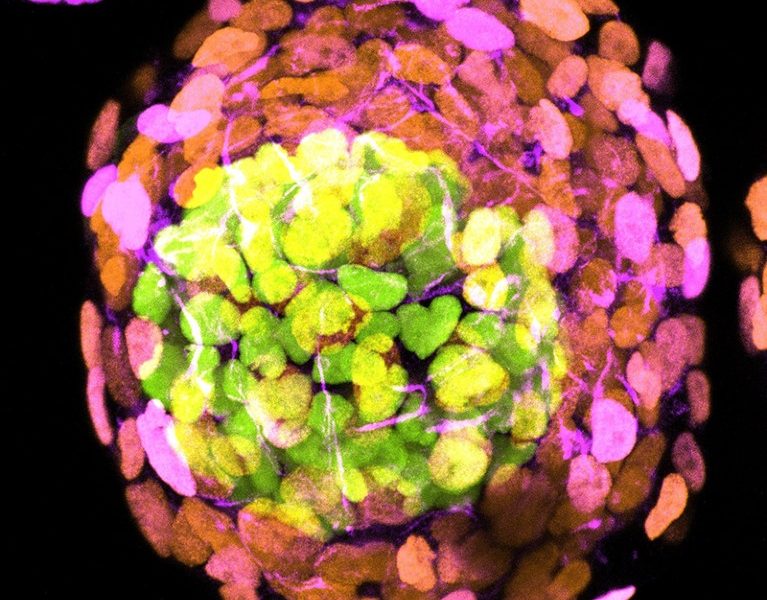
Two teams of scientists have introduced that they have expanded embryo-like structures, made totally from human stem cells, that are more advanced than any kind of previous initiatives. The artificial embryos developed to a stage comparable to that of natural embryos about 2 week after fertilizing.
Such experiments can give possibilities to research human beginning advancement at later stages than ever. Yet they additionally increase ethical and legal questions regarding the condition of such ’em bryo models’ and also just how they should be controlled.
The job is described in two preprint studies1,2, uploaded to the bioRxiv web server on 15 June by groups led by developing biologist Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz at the College of Cambridge, UK, and also stem-cell biologist Jacob Hanna at the Weizmann Institute of Scientific Research in Rehovot, Israel. Both groups had formerly provided their searchings for at scientific meetings, with the work making headlines after Zernicka-Goetz mentioned her outcomes at the yearly meeting of the International Culture for Stem Cell Study in Boston, Massachusetts, on 14 June.
Nature spoke to scientists about what these growths could mean for study on human embryos.
What did the researchers do and just how does it vary from previous work?
Both groups permitted their embryo-like structures to self-assemble from human beginning stem cells, several of which had actually been exchanged cell kinds appearing like the stem cells that form a placenta and the cells that form the yolk sac outside a naturally creating embryo.
The scientists claim that the resulting embryo designs reveal frameworks and also genetics transcription accounts located in human embryos in between 6 and 14 days after fertilization– up to the start of the phase called gastrulation, when the cells that will certainly develop the embryo become arranged into a layer in between the amniotic dental caries as well as the yolk cavity.
Researchers have made comparable entities before from the stem cells of people as well as various other animals. In 2014, both Zernicka-Goetz’s and also Hanna’s groups utilized similar strategies to create embryo models from mouse cells that developed right approximately the phase at which body organs such as the heart as well as mind begin to form3,4. Human embryo designs haven’t got that much, but in a preprint uploaded on bioRxiv on 17 Might, stem-cell biologist Ali Brivanlou at the Rockefeller College in New York City and also his co-workers reported the development of human embryo versions that reveal signatures of gastrulation equivalent to those seen at around 12 days after fertilization5. The most recent studies1,2 say that they have made the most sophisticated human embryo models until now.
What is the relevance of the embryos lasting for 2 week?
Study on natural human embryos often tends to observe a widely embraced standard– enforced by regulation in lots of nations– that human embryos should not be cultured in the laboratory past 2 week. This suggests that scientists need to use animal designs to research later phases of embryonic advancement. These do not necessarily mirror the equivalent procedures in human beings.
Yet because in many nations embryo versions do not fulfill the official meaning of an embryo, they are exempt to such restrictions. “We looked for to develop a tool to ask particular questions regarding the second week of human embryo development, since utilizing real human embryos in research is ethically and also technically tough,” states Zernicka-Goetz.
Models that are older than 2 week might as a result use crucial understanding right into human beginning advancement that can not presently be acquired. They can be made use of to study developmental defects, for instance, or pregnancy loss.
Why is the study medically debatable?
Expanding embryo versions to ever-later stages of development has actually ended up being a very affordable race, provoking many disagreements concerning the values of claims made.
It continues to be to be seen whether the cases made by the most recent research studies, neither of which has actually yet been peer-reviewed, will certainly pass muster. Alfonso Martinez Arias, a developmental biologist at Pompeu Fabra College in Barcelona, Spain, claims there is “absolutely nothing” in the outcomes defined by Zernicka-Goetz as well as her colleagues that can be considered similar to genuine 14-day embryos. “What we can see is masses of cells divided into compartments, but no embryo-like organization,” he says. He thinks that the over-expression of some genetics needed to produce the extra-embryonic cell types “confuses what cells do”, and says that the results do not show anything that goes beyond earlier work.
Zernicka-Goetz recognizes the restrictions of embryo versions for studying growth. “These structures do not recapitulate all elements of the embryo,” she states, “however rather serve as a corresponding tool for us to research the differentiation of specific cells during crucial stages of advancement.”
What regarding honest worries?
The outcomes have actually triggered a conversation regarding the standing of human embryo models in general, and also whether they need to continue to fall outdoors regulation on human embryos. Although they are exempt to the 14-day rule, the embryo-like frameworks reported by Zernicka-Goetz’s and also Hanna’s teams do require to respect guidelines as well as regulations on the use of the human beginning stem cells from which they are made. But various other groups have actually made embryo models using ‘induced’ stem cells originated from adult tissues6, which are not regulated by such policies. Those embryo designs “are not controlled whatsoever”, claims Robin Lovell-Badge, a cell biologist at the Francis Crick Institute in London.
Up until now, no one has made embryo designs that have the capacity to turn into people, yet a recent research on ape embryo designs showed that such designs can generate maternity (which ended automatically right after) if put in the uterus7.
Some scientists believe that a modified definition of an embryo is needed to make clear the concerns. For others, the whole function of embryo versions is to prevent the present restraints on embryo research. “These versions do challenge the need to adhere to the 14-day policy,” claims Lovell-Badge, who became part of a committee that, in 2021, recommended loosening up the standard.
Regardless, there are significant challenges to making human embryo models that live a lot longer, claims Martinez Arias. Producing structures that establish approximately 21 days “will certainly not be easy”, he claims. “I will be surprised if [human embryo models] can go beyond it.”





No Comment